Understanding what is Options Trading: Options are one of the highly traded financial instruments and darling of the big traders and investors. However, for beginners, understanding what is options trading is one of the biggest difficulties because of its complexity (which comes by nature) and the difficult jargon used by the experts.
In this article, we’ll discuss exactly what is options trading and how it works with the help of a few examples. Let’s get started.
What is Options Trading?
Options are financial instruments whose value is derived from the value of an underlying or involved asset like stocks, commodities or any other asset. It gives the Options buyers a right to buy the underlying asset at a pre-decided price from the option seller on or before a pre-defined date (also known as the expiry day).
However, here, the options buyer is not obligated to honor the contract upon expiry i.e. he has the right to buy the asset only if he chooses to. Nonetheless, the Options Seller is obligated to honor the contract.
This is because the option seller receives compensation in the form of this fee (also known as the premium) to give up his right to underlying assets till the expiry of the contract. If the buyer does not want to buy the asset from the seller, he will simply lose the premium paid beforehand. Options trading is the system of buying or selling these options contracts.
Now, let us understand this better with the help of an example.
An example to Understand Options
Imagine Mohan has a wedding in his house after four months and wants to buy gold for the same. However, he is fearful of the fact that the gold price might go up in the future. Therefore, to protect himself from the risk of price fluctuations, he goes to a Jewelry shop, and enters into an agreement with the shop owner whereby he fixes the price for jewelry for buying four months down the line, at the current price of Gold.

But, you must be wondering as to, what is the incentive here for the Jewelry shop owner to fix the price because he is potentially taking a big price risk. If the price goes up after four months, still he’ll have to sell the jewelry at the pre-determined price. Here, his incentive is a small fee (i.e. Premium/Token) that he will be charging to Mr. Mohan for fixing the price of gold. And this fee here is non-refundable.
Say, four months down the line if the price of gold goes up then Mr. Mohan has the right to buy gold at the pre-decided price. On the other hand, if for some reason the price of gold comes down then he does not have to exercise his right, i.e. he may choose to buy jewelry from some other shop at the discounted current price. He merely stands to lose his premium/token.
Who are Options Buyers and Sellers?
An option buyer is a trader/investor who buys the option from the seller. It means that the buyer buys the right to buy an underlying asset at a pre-decided price from the seller on or before expiry. The option buyer pays a premium (fee or compensation) to the options seller for this contract and hence is not obligated to exercise the option, unlike the seller.
Options buyers have limited risk (i.e. only up to the premium paid), however, the potential reward is unlimited to them theoretically.
On the other hand, Options sellers are those investors or traders, who receive the premium from the buyer to get into the agreement and have the obligation to honor the contract if the buyer wishes to exercise the option before expiry. Options sellers are also known as Options writers.
Note: Want to learn Options Trading from Scratch? Enroll in this best-selling Options trading course at FinGrad
Why would an investor use options?
When an investor or trader is buying an options contract, he/she is betting on the price to go in his favor. The price at which one agrees to buy the involved asset via the option is called the ‘Strike price’ and the price paid for having this right is called the ‘Options premium’.
Also Read: 21 Key Options Trading Definitions – Must Know Options Terms for Beginners!
Breaking Down Call and Put Options
The Call and Put options are the types of options that help traders and investors to capitalize on their views. Depending on the views (bulling or bearish), an options trade can buy or sell a Call or Put Option. Now, let us understand both of these ‘Call’ and ‘Put’ options in detail.

What is Call Option?
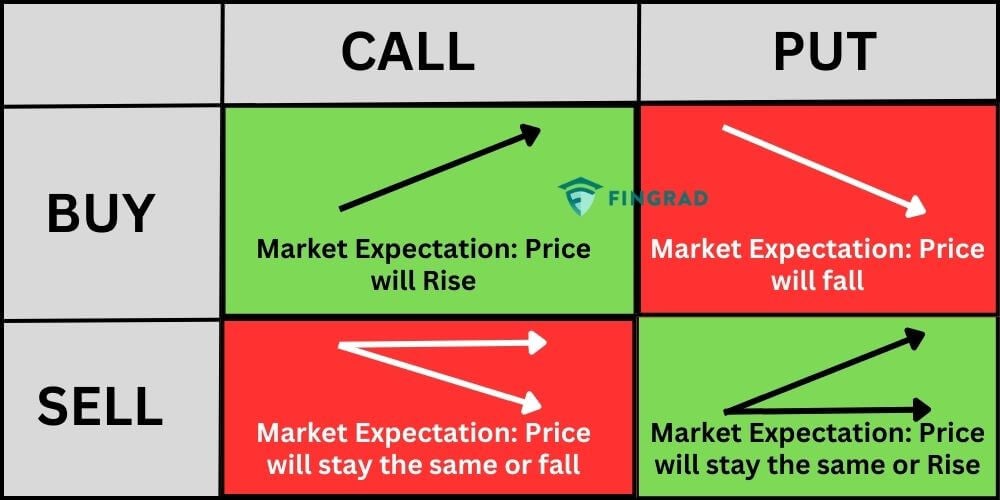
A call option is a type of option that gives the buyer the right to buy an underlying asset at a pre-determined price at a future date. The buyer of a call option generates profits only when the value of the underlying asset is rising upwards.
Basically, the real purpose of buying a call option is that the trader is expecting the price of the involved security to move up in the near future.
On the contrary, the trader who sellers (or writes) a call option, has an opposite (bearish) view that the price of the asset will not go higher than that pre-determined price.
What is Put Option?
A Put option is a type of option that gives the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at a pre-determined price at a future date. The buyer of a put option generates profits when the value of the underlying asset is falling.
In simpler terms, a trader or investor buys a put option when he expects the price of the involved asset to fall in the near future. The trader who sells (or writes) a put option has an opposite (bullish) view that the price of that asset will not go below that pre-determined price.
Benefits of Options Contract
Here are a few key benefits of Options contracts:
- As the name would suggest, the Options contract gives the right to option buyer to exercise his contract if he wishes to. If the current price doesn’t go in favor of the buyer of the contract he does not have to exercise his right, he stands to lose just the premium.
- The one-time premium is the only fee that the option buyer has to pay to ride the momentum of the underlying price and be a part of a bigger game.
- For example, if a trader wants to buy 1000 shares of Reliance, then at the current market price (Rs 2,400 per share), one has to shed out Rs 24,00,000 (Twenty-four lakhs). But one can express the same view by buying Call/Put option contracts with 2 lot sizes of 500 shares each).
- If an option seller is of the opposite view to that of an option buyer, he can just sell the option contract and market profits through the premium received.
- Return on investment for an option buyer is very high because the cost paid is just the premium and the potential return is unlimited.
Closing Thoughts
In this article, we have discussed what is options trading, how it works, and two types of options i.e. Call Option and Put Option.
To Summarize, an option is a contract that provides the buyer an option but not obligation to buy or sell the involved security or asset at pre-decided price within the contract expiration time. For traders and investors, it gives the power of leveraging with limited money as options are cheaper to purchase compared to buying a same number of shares in the marketplace.
The real purpose of buying a call option is that the trader or investor is expecting the price of the involved security to move up in the near future and vice versa for the call option seller. On the other hand, A Put option is bought by the trader or investor when he expects the price of an involved asset to fall in near future and vice versa for put option seller or writer.
The post Options Trading 101: What is Options Trading? appeared first on Trade Brains.
Viahttps://ift.tt/I0Em9qX